Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by the body’s inability to regulate blood sugar. It develops when the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin for the body or does not respond to the insulin produced effectively. Diabetes affects children, including newborns and adults. It is, however, a manageable condition with the right lifestyle changes and medications.
What Are the Different Types of Diabetes?
 There are different types of diabetes. They include:
There are different types of diabetes. They include:
- Prediabetes: is an early stage of type 2 diabetes where your blood glucose levels are higher than they should be but not high enough for an official diabetes diagnosis.
- Type 2 diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes. This occurs when the body does not make enough insulin or its cells do not respond as they should to the insulin, also known as insulin resistance.
- Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells. It is often diagnosed in children and young adults but can also develop at any age.
- Gestational diabetes: This type of diabetes develops during pregnancy and often goes away after gestation. However, if you develop gestational diabetes, you are likely to develop type 2 diabetes in the future.
How Is Diabetes Diagnosed?
Diabetes is diagnosed by checking blood sugar levels. It is commonly done using four of the following tests.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: This test involves measuring the sugar levels before and after drinking a glucose beverage. A result of 11.1 mmol/L (200mg/dl) or higher indicates diabetes.
- A fasting blood glucose test requires you not to drink or eat anything except water for eight hours before the teats. Food will affect your test results, and you must provide a baseline for your blood sugar. A level of 7.0 mmol/L (12 mg/dl) or higher indicates diabetes.
- The A1C test: The glycated hemoglobin test or HbA1 test, the A1C test provides an overview of the blood sugar levels during the past two to three months. A level above 6.5% on separate tests indicates that you have diabetes.
- Screening: The (ADA) American diabetes association recommends routine screening for type 2 diabetes for adults over 35 years who are overweight, have had gestational diabetes before, or have already been diagnosed with prediabetes before.
How Is Diabetes Treated?
 Diabetes is a complex metabolic disorder, and its management involves several strategies. Every patient has a highly customized diabetic management plan based on their needs. Here is how to manage and treat diabetes:
Diabetes is a complex metabolic disorder, and its management involves several strategies. Every patient has a highly customized diabetic management plan based on their needs. Here is how to manage and treat diabetes:
Through Medication
Diabetes can be treated through oral medication and insulin injections to help manage the condition. Oral medication is often prescribed to patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, while insulin injection is for patients with type 1 diabetes.
A Healthy Diet
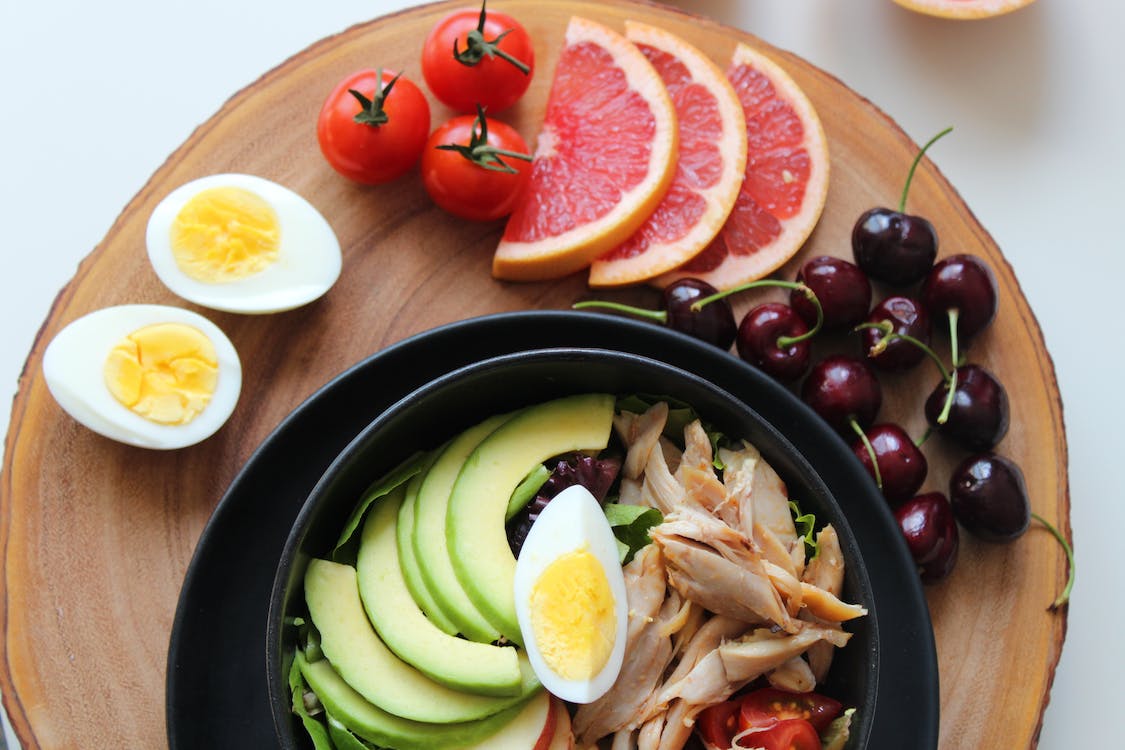
Your diet is a huge part of diabetes management. If you have diabetes, you will have to choose a healthy diet. You must add food in soluble and insoluble fiber, leafy greens, and fruits low in sugar content. You must also avoid sugary drinks as much as possible to prevent your blood sugar levels from spiking.
Physical Exercise
Studies have shown that physical activity increases insulin sensitivity. Therefore, regular exercise is an essential part of managing diabetes.
How Can I Prevent Diabetes?
You cannot prevent the genetic and autoimmune forms of diabetes. You can take steps to lower your chances of developing prediabetes, gestational diabetes, and type 2 diabetes. These include:
- Get physical activity, at least 30 minutes daily, at least five days a week.
- Adopt a healthy diet
- Work to achieve a healthy weight
- Limit your alcohol intake
- Manage your stress
- Get enough sleep, around 7 to 9 hours, and get treatment if you notice you have a sleeping disorder
- Reduce or quit smoking
- Ensure you take medication as directed by your doctor to manage any risk of heart disease.
Are you looking for ways to monitor and manage type 2 diabetes? Visit Columbia Medical Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems (CGMS). We are experts in continuous glucose monitoring devices to help you manage Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes with no finger sticks! We will help you devise the perfect plan to manage your condition to improve your quality of life.
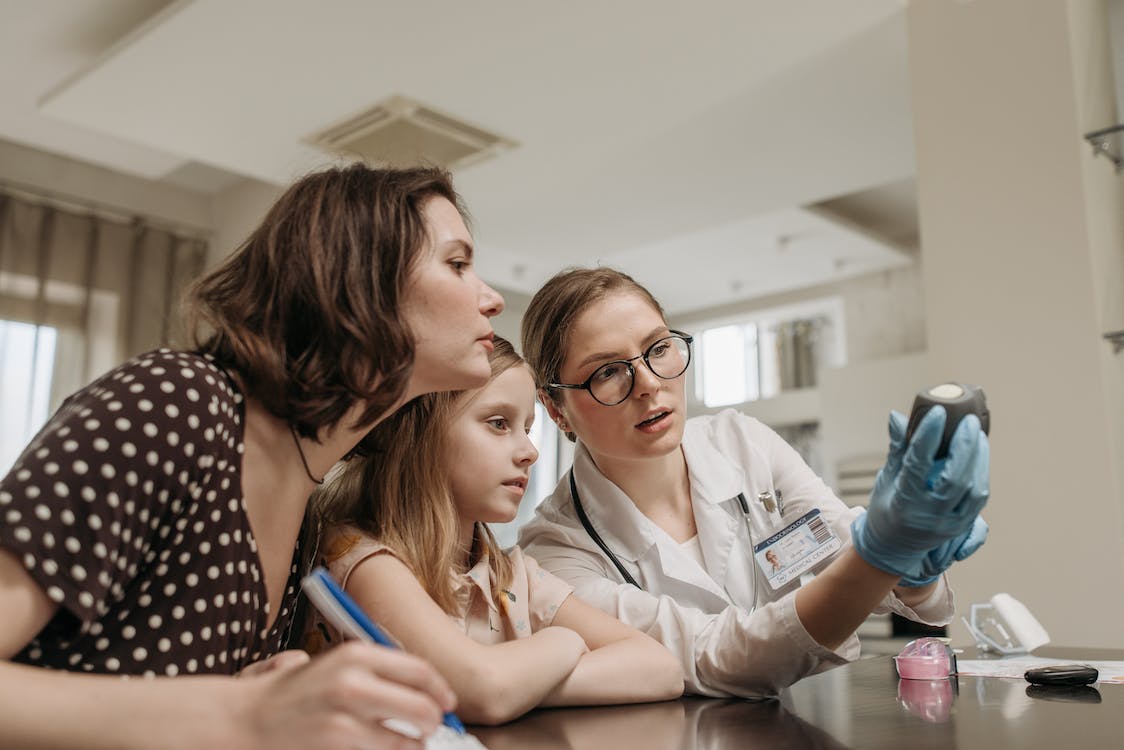
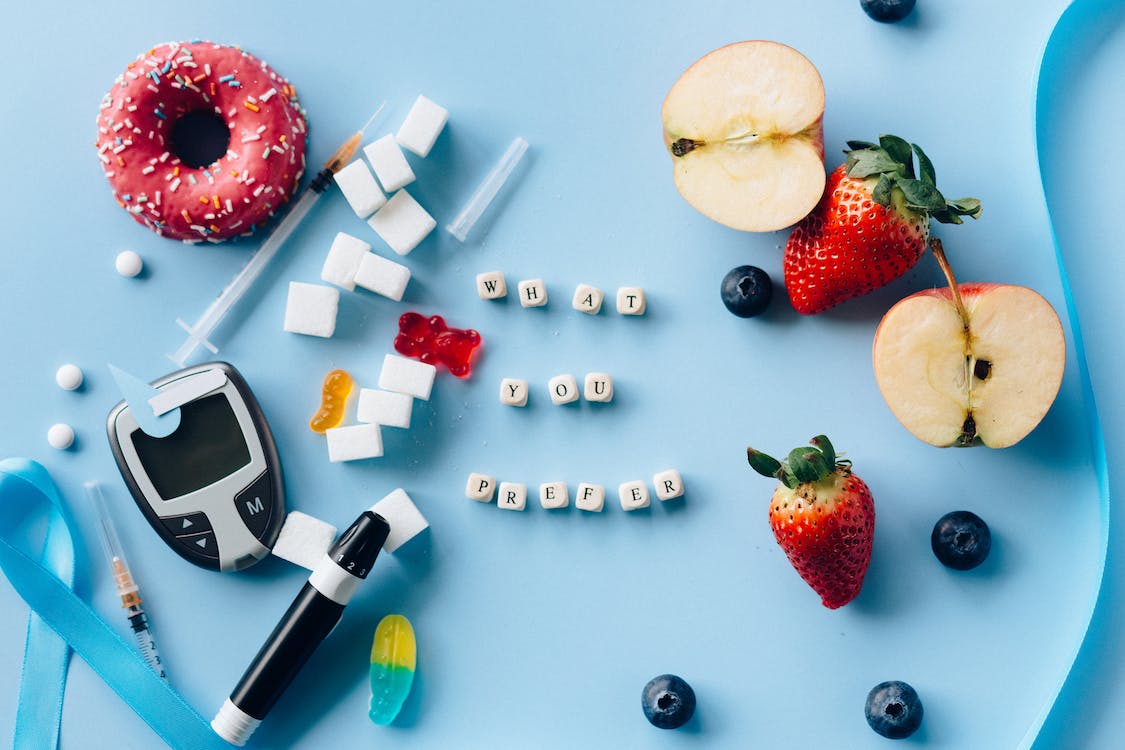






 We are experts in Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems (CGMS). Our CGM devices will help you efficiently manage Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes with No Fingersticks!. Abbot’s Freestyle Libre System will track the glucose levels in your blood and help you determine how much insulin you will need and when you will need it!
We are experts in Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems (CGMS). Our CGM devices will help you efficiently manage Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes with No Fingersticks!. Abbot’s Freestyle Libre System will track the glucose levels in your blood and help you determine how much insulin you will need and when you will need it!